Introduction

Aging is a natural process, but did you know that oxidative stress can accelerate this process? Through this blog, you will understand the detailed relationship between oxidative stress, aging, and stress management so that you can create better strategies against oxidative stress and healthily enjoy your natural aging process.
Let us know what oxidative stress is:
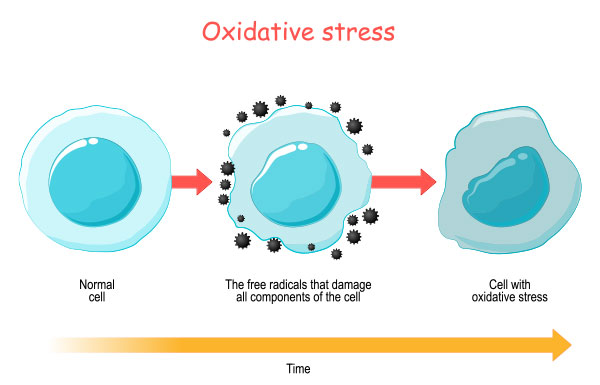
An imbalance between antioxidants and free radicals in your body can lead to oxidative stress. Oxygen-containing molecules known as free radicals have an uneven electron count, which makes it easy for them to react with other molecules. These reactions have the potential to harm DNA, proteins, and cells, which can accelerate aging and lead to a number of illnesses.
Free radicals are spontaneously produced by the body during metabolic activities. However, outside variables including radiation, pollution, nutrition, and cigarette smoke can also raise the levels of free radicals. Antioxidants are compounds that can neutralize free radicals and lessen their detrimental effects. They are created by the body and can be found in certain foods.
The Impact of Oxidative Stress on Aging

It has a role in the beginning and advancement of age-related illnesses such as diabetes, Alzheimer’s disease, and cardiovascular disease. Furthermore, by destroying crucial biological components like lipids, proteins, and DNA, oxidative stress might have an impact on how quickly we age.
The effect of oxidative stress on telomeres, which act as protective caps at the ends of chromosomes, is one of the main characteristics associated with aging. Age-related health problems are more likely to arise because oxidative stress promotes the telomere-shortening process, which speeds up cellular aging.
How to Manage Oxidative Stress
Managing oxidative stress involves lifestyle changes and strategies that reduce the production of free radicals and enhance your body’s antioxidant defenses:
Strategies for Handling Oxidative Stress: Changing how you live and applying tactics that lower free radical generation and strengthen your body’s antioxidant defenses are necessary to manage oxidative stress:
Antioxidant-Rich Diet: It’s important to eat a diet rich in antioxidants. Eat as much fruit as possible, such as oranges and berries, as well as whole grains, nuts, and seeds, and veggies like bell peppers and spinach, you can also take antioxidant supplements. Your body’s defenses against oxidative stress are strengthened by these nutrients.
Frequent Exercise: Regular exercise raises your immune system’s antioxidant levels and aids in reducing the generation of free radicals. Exercises such as swimming, yoga, cycling, using meditation apps, and brisk walking can be especially helpful.
Stress Reduction Strategies: It’s critical to use stress reduction strategies like yoga, meditation, reading books on how to deal with stress, and deep breathing practices because psychological stress can worsen oxidative stress.

Sufficient Sleep: Lowering oxidative stress involves getting enough hours of sleep every night. Your body may recover and repair itself as you sleep, which minimizes oxidative damage.
Avoiding Harmful Exposures: Reduce your exposure to cigarette smoking, pollutants from the environment, and too much sunshine as they can raise the levels of free radicals around your body.
FAQs on Oxidative Stress and Aging
- How does oxidative stress affect mental health? Oxidative stress is linked to the development of mental health conditions like depression and anxiety by damaging brain cells and altering neurotransmitter levels.
- Can antioxidant supplements help reduce oxidative stress? While a diet rich in antioxidants is preferred, supplements can also help, especially if dietary intake is insufficient. Consult with a healthcare provider before starting any supplement regimen.
- What are some signs of high oxidative stress levels? Common signs include fatigue, memory loss, muscle or joint pain, wrinkles, and decreased eye health.
- Are there any tests to measure oxidative stress? Yes, there are several biomarker tests available that can assess oxidative stress levels, such as tests for malondialdehyde (MDA) or advanced oxidation protein products (AOPPs).
- How do antioxidants neutralize free radicals? Antioxidants donate an electron to a free radical without destabilizing themselves, thus stopping the chain reaction of damage.
Understanding oxidative stress and its effects on aging is crucial for maintaining health as you age. By integrating effective strategies to manage oxidative stress, you can enhance your quality of life and potentially slow the aging process.